Bathing
Select a Skill:
- » Performing a Complete or Partial Bed Bath
- » Assisting with a Tub Bath or Shower
- » Performing Back Massage
- » Performing Perineal Care for a Female Patient
- » Performing Perineal Care for a Male Patient
Take the Review Test:
Safety
- Assess the patient's fall risk status, consider patient's condition, and review orders concerning precautions to observe in the patient's movement or positioning.
- Wear clean gloves if you identify drainage or secretions on the patient’s skin.
- Take measures to prevent falls, such as placing a rubber mat on the tub or shower floor, using a tub chair or shower seat, and instructing the patient to use the grab bars. Do not use bath oil in the tub water.
- Do not massage any reddened area on the patient’s skin.
- Check the temperature of the bath water or shower, and adjust it if it is too warm or too cold.
Equipment
(Roll cursor over items to see labels)
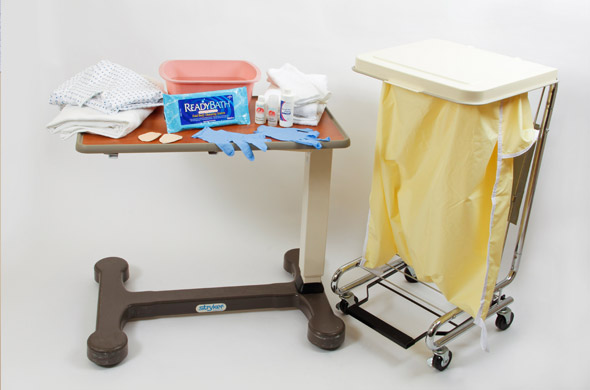
Bath towels
Toiletries, such as deodorant and lotion
Clean hospital gown or patient's own pajamas
Linen bag
Clean gloves
Washbasin
Disposable bath-in-a-bag product
Delegation
The skill of bathing a patient in the tub or shower can be delegated to nursing assistive personnel (NAP). Before delegating this skill, be sure to inform NAP of the following:
- Stress the importance of not massaging reddened skin areas during bathing.
- Explain how to properly position male and female patients with musculoskeletal limitations.
- Remind NAP to report to you any changes in the skin or perineal area or any signs of impaired skin integrity.
Preparation
- Assess the environment for safety, such as checking the room for spills, making sure equipment is working properly, ensuring that the bed is in the locked, low position, and providing privacy.
- Explain the procedure, including precautions taken to reduce falls and provide privacy.
- Assess the patient’s fall risk status, consider the patient’s condition, and review orders concerning precautions to observe in the patient’s movement or positioning. A physician’s order is usually needed for a tub bath or shower.
- Schedule use of the shower or tub.
- Check the tub or shower for cleanliness. Use cleaning techniques outlined in agency policy.
- Place a rubber bath mat on the tub or shower bottom. Place a skidproof disposable bath mat or towel on the floor in front of the tub or shower. Use a tub chair or shower seat and instruct the patient to use the grab bars.
- Collect all hygienic aids, toiletry items, and linens requested by the patient. Place them within easy reach of the tub or shower.
- Do not use bath oil in the tub water.
Follow-up
- Determine the patient’s comfort and level of fatigue.
- Inspect for signs of skin breakdown, irritation, and infection, and take steps to prevent them.
- Report signs of altered skin integrity to the nurse in charge or to the health care provider.
Documentation
- Record the tub bath or shower, noting the level of assistance needed and how the patient tolerated the procedure.
- Record the condition of the skin and any significant findings, such as reddened areas, discharge, bruises, nevi, and joint or muscle pain.
- Report any evidence of altered skin integrity, breaks in the suture line, or increased wound secretion to the nurse in charge or to the health care provider.
Review Questions
1. Which nursing action reduces the risk of falling as a patient is getting into or out of a bathtub?
 Add 1 oz of bath oil to the tub water before the patient gets into the tub.
Add 1 oz of bath oil to the tub water before the patient gets into the tub.  Place an “Occupied” sign on the bathroom door.
Place an “Occupied” sign on the bathroom door.  Fill the tub half full of water at 110°F-115°F.
Fill the tub half full of water at 110°F-115°F.  Place a skidproof disposable bath mat in front of the tub.
Place a skidproof disposable bath mat in front of the tub.
2. A patient with left-sided muscle weakness is prescribed a bath every other day. Which precaution would help the nurse reduce this patient’s risk of falling?
 Maintain the water temperature at 104°F.
Maintain the water temperature at 104°F. Allow the patient to remain in the bath for 45 minutes.
Allow the patient to remain in the bath for 45 minutes.  Decline the patient's request to add scented oil to the bathwater.
Decline the patient's request to add scented oil to the bathwater.  Discuss the patient's level of fatigue after the bath.
Discuss the patient's level of fatigue after the bath.
3. The nurse has just helped a patient into the bathtub. Before leaving the bathroom, what would the nurse do to help ensure the patient's safety?
 Show him how to use the call signal.
Show him how to use the call signal. Place an “Occupied” sign on the door.
Place an “Occupied” sign on the door.  Check the cleanliness of the room.
Check the cleanliness of the room.  Remove unneeded supplies from the bathroom.
Remove unneeded supplies from the bathroom.
4. The nurse is assisting a patient with a tub bath. After the patient has been safely positioned in the tub, he tells the nurse, "I'll call you when I'm done." What is the nurse's best response?
 "All right. Just holler when you're ready, and I'll come help you get out of the tub."
"All right. Just holler when you're ready, and I'll come help you get out of the tub." "Well, I'll check back with you in about 5 minutes to see if you need anything."
"Well, I'll check back with you in about 5 minutes to see if you need anything." "That's not safe. I'll wait right outside the door for you to finish."
"That's not safe. I'll wait right outside the door for you to finish." "I'll be back in 15 minutes. That should be enough time for you to finish up."
"I'll be back in 15 minutes. That should be enough time for you to finish up."
5. The nurse is helping a patient get out of a bathtub, and the patient appears to be unsteady on her feet. What should the nurse do to help ensure the patient’s safety?
 Drape a bath towel over the patient’s shoulders.
Drape a bath towel over the patient’s shoulders.  Demonstrate how to use the call light for assistance.
Demonstrate how to use the call light for assistance.  Drain the bathtub before the patient gets out.
Drain the bathtub before the patient gets out.  Apply lotion to the patient's freshly dried skin.
Apply lotion to the patient's freshly dried skin.
You have completed the Review Questions for this skill. To take the Review again select the Start Over button. To proceed to another skill select from the dropdown menu. Select the Home or Back button to proceed to the next section.

